Genital warts can settle on the labia minora, labia majora, in the clitoral area, at the vaginal introitus, between the vagina and the anus, which is called “perineum”, around the anus. The incidence rates in women and men are similar.
What are Genital Warts? How are They Transmitted? Treatment of Genital Warts
HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) infections cause genital warts and cancers in the genital area in women. In men and women, warts in the genital area can spread and cause cosmetic problems, and can also pass to the partner. It also causes psychological problems. In this section, you can find detailed information about genital warts.
Answers are sought especially for frequently asked questions such as "why do genital warts develop, how is genital wart treatment performed, how are genital warts treated with laser".
What are genital warts?
The most common symptom of HPV infection is warts located in the genital area and around the anus.
Genital warts can settle on the labia minora, labia majora, over the clitoral area, at the entrance to the vagina, between the vagina and the anus, which we call the perineum, and around the anus. It can also develop in the vagina, cervix and rectum (lowermost portion of the large intestine).
Genital warts are not just a cosmetic problem because they can also cause serious psychological problems in people due to their rapid spread, transmissibility to partners, as well as their spread to different parts of the body skin-to-skin contact. In addition, they can turn into marital problems that lead to divorce. The incidence rates in women and men are similar.
How are genital warts transmitted?
Genital warts are most commonly transmitted through sexual intercourse. Vaginal, anal or oral sex, and sharing sexual toys are the main ways of transmission.
What is a condyloma? (Condyloma Acuminata)
Warts are skin outgrowths caused by the rapid growth of cells on the outer layer of the skin. If genital warts are in the form of clustered large lesions, they are called “condyloma”. Condylomas (Condyloma acuminata) can be “cauliflower-shaped” and in different sizes.
Warts caused by HPV can be located on different parts of the body. Warts can also be seen in wide, flat and plantar areas (e.g. the sole surface).
Where do the genital warts locate?
Genital warts can appear around the anus, vulva (external genital area),vagina, cervix and rectum. Therefore, they are also called ‘anogenital warts’.
The types of HPV that cause genital warts are different from HPV-related warts, which develop in other parts of the body. HPV types 6 and 11 are responsible for 90% of genital warts. These types are in the low oncogenic risk group. Genital warts neither cause cancer nor turn into cancer!
Do warts proliferate more during pregnancy?
Genital warts can proliferate during pregnancy. This is caused by the changes in the immune system. Due to the weakening of the immune system, latent HPV infections can get activated.
Although genital warts do not constitute an obstacle to vaginal delivery, the presence of common warts may require cesarean section.
How are they diagnosed?
Generally, they can be easily diagnosed during visual examination. In suspicious cases, a biopsy is performed and the diagnosis is confirmed through pathological examination. In most people, genital warts do not cause any complaints, and in some cases they show symptoms with only mild itching.
Who suffer from HPV Infections most commonly?
The distribution of HPV infections varies across the world. This may be due to age, gender, anatomical region, but is also associated with socioeconomic, cultural and genetic factors. People in developing countries are more commonly exposed to HPV infection. For example; approximately half of women in Asian countries are HPV carriers. When evaluated in terms of age, it is more common among women under 25 years of age.
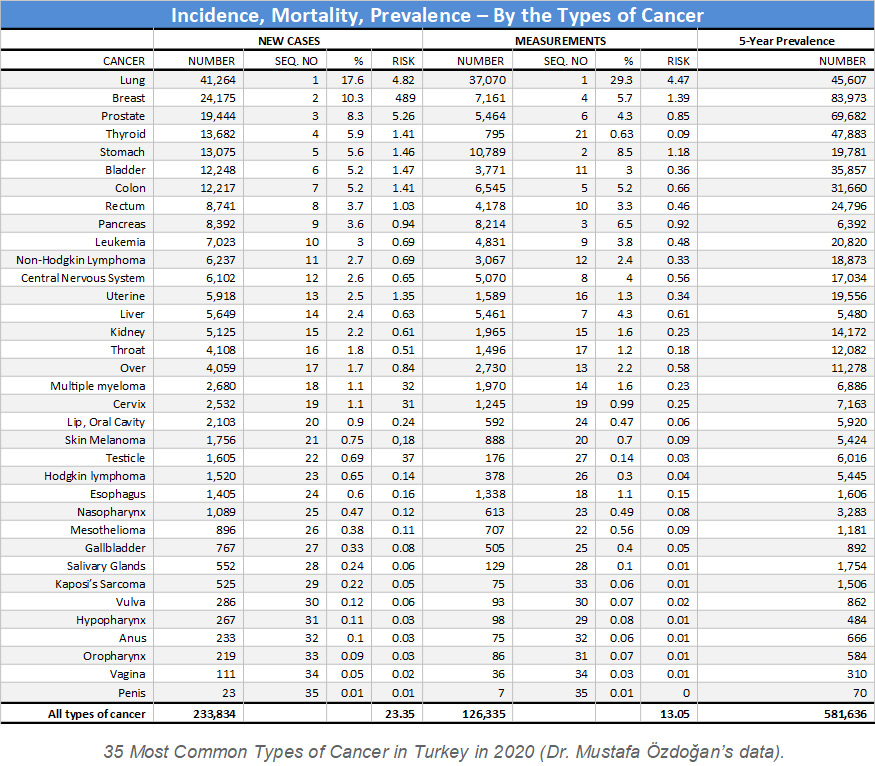
HPV is a preventable cause of cancer. Cervical cancer ranks 19th among all types of cancers in Turkey and 3rd among gynecological cancers after uterine and ovarian cancers. Almost all cervical cancers develop in consequence of HPV infection. Therefore, it is important to perform HPV screening tests in the community, and to maintain the follow-up processes for people found to be infected, by taking the necessary precautions.
How are HPV tests performed?
Today, detecting HPV DNA in the cervical swab sample is the only method intended for this purpose. Early diagnosis is important because it may lead to cancer if precautions are not taken. The most important tests used in screening for this purpose are Smear and HPV tests. Both tests can be performed in the same session when the patient is on the gynecological examination table.
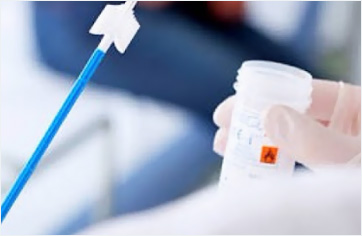
After the insertion of a sterile examination instrument (speculum) into the vagina, a sterile thin swab is swept gently over the surface. The swab samples taken are sent to the genetic laboratory for PCR tests and analyses. HPV testing is an extremely painless procedure. With this test procedure, the potential presence of HPV is investigated. This test is also used to determine the HPV type in patients who tested positive.
How often should the scans be performed?
Screening protocols vary depending on the woman’s age, screening history, and risk factors. Routine screening with a smear test + HPV test every 5 years or with a smear test alone every 3 years would be adequate. HPV screening is started after 30 years of age. This is because the virus is expected to be cleared from the body until this age.
If HPV infection is detected in a patient over 30 years of age, further examinations are definitely necessary. Patients with warts are in the patient group that should be evaluated carefully in terms of high-risk HPV types. Therefore, smear and HPV tests are required for these patients.
In smear scanning, cervical cells are checked for abnormalities. If the smear test gave a normal result and the HPV test result is negative, routine screening would be adequate. However, in patients who tested positive for HPV, the cervix should be evaluated in detail. If the smear is not adequate for this, a colposcopy can be performed as well.
What is a colposcopy?
It is an examination performed on patients, whose smear test or speculum examination showed a suspicious appearance in the vagina or cervix. Magnified views of the vagina and cervix obtained with a magnifying device are examined with a camera system. Tissue samples taken (biopsy) from the required areas are sent to laboratories for pathological examination. Thus, it can be possible to diagnose genital cancers at an early stage.
Treatment of Genital Warts
Today, there is no specific treatment for HPV infection. It usually disappears spontaneously within a period of 2 years. However, some commonly encountered warts may require surgical or non-surgical interventions.
The procedures most commonly performed for the treatment of genital wart:
- Burning with electricity (electrocauterization),
- Freezing (cryotherapy),
- Burning with laser,
- Treatment with acid solutions.
Large lesions, especially large condylomas can be surgically removed.
Genital Wart Treatment by Laser
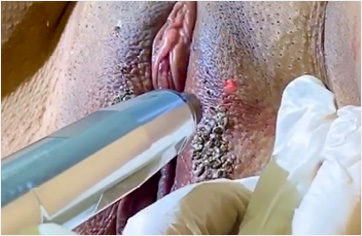
Laser treatment for warts is highly effective. It gives results in a short time. It is extremely painless, and has a very low risk of leaving scars after treatment. The procedure that takes 4-5 minutes on average allows for cleaning the whole genital area comfortably under local anesthesia (by numbing the application area). Because of these features, it is more advantageous than other treatment procedures.
Picture shows genital wart treatment by laser coagulation.
In our Istanbul (Nişantasi and Bagdat Caddesi) and Ankara clinics, genital wart treatment for women and men is performed with CO2 lasers.
After Wart Treatment
The point to remember is that none of these treatments eradicate HPV infection, but warts only. If hygiene rules are not followed properly and measures are not taken to increase body resistance, HPV continuing to exist under the skin will get reactivated and form warts. Therefore, it is important to strengthen the immune system and even take precautions with vaccination before any possible transmission with HPV.
Close follow-up is planned for HPV infections detected during routine cervical cancer screening tests. If there is any cellular abnormality in the cervix, cancer development can be prevented with simple surgical interventions such as conization and LEEP procedures.
HPV Infection and Cancer
Anal, vulvar, oropharyngeal cancers, as well as more than 90% of anogenital cancers are associated with HPV. In addition, almost all cervical cancers (99.7%) are caused by HPV infection. Fortunately, not every HPV infection in the cervix becomes cancerous immediately. It is usually eliminated by the immune system. However, if defense is insufficient, high-risk HPV types can continue to remain in the body for a long time and cause cellular changes that can lead to cancer.
Studies have revealed that the process leading to cancer in consequence of HPV infection is a long process that takes 10-20 years. Especially HPV types16, 18, 31 and 45 have carcinogenic potential, that is, they tend to cause cancer.
The virus that cannot be controlled by the immune system may also lead to penis, head, neck and skin cancers. Moreover, studies have revealed that some types of lung cancer are also associated with HPV.
Do genital warts cause cancer?
HPV types which cause genital warts are in the low risk group. Therefore, warts do not become cancerous or patients with genital warts are not at a greater risk of cancer. However, the presence of high-risk HPV types in the body at the same time increases the risk of cancer. If HPV carriers are also smokers, the risk of cancer increases even more. In addition, having a family history of cancer increases the risk of cancer. Therefore, it is important to carry out routine follow-up of every patient, who has had HPV infection, by performing screening tests.